Introduction to Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has become a popular technology forusinesse organizations in recent years. It has enabled them to improve efficiency, scalability, and flexibility while reducing costs. This article will explore cloud computing, its key components, types, advantages and disadvantages, steps involved in implementing it, security concerns, case studies, and best practices.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is a delivery computing resources over the internet on demand. It enables businesses and individuals to use computing resources such as servers, storage, applications, and services without physical infrastructure. Cloud computing allows users to access data and applications from any device with an internet connection.
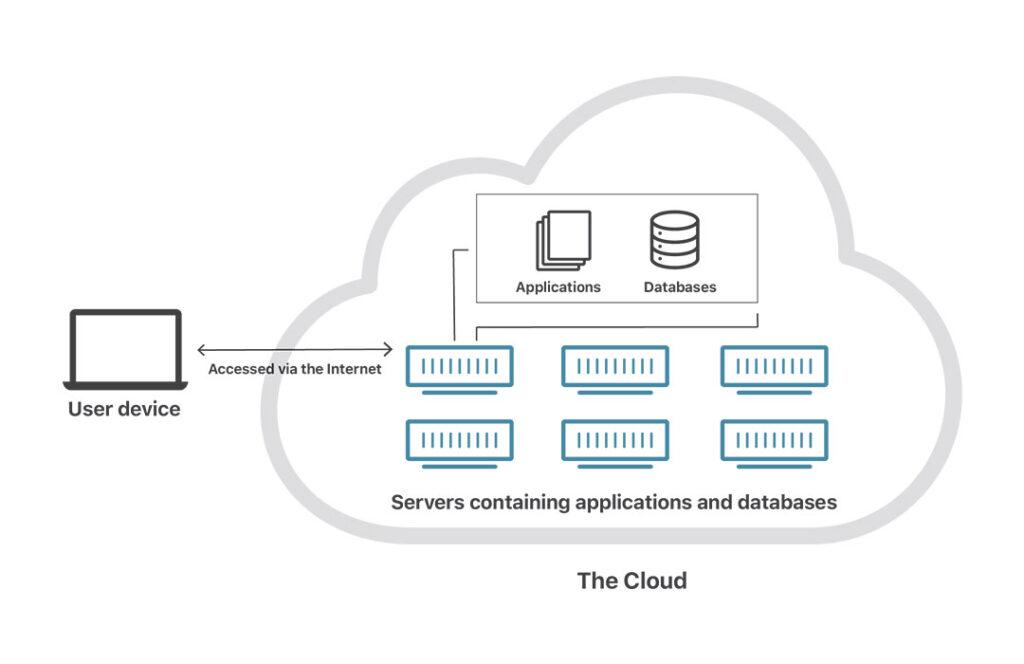
Key Components of Cloud Computing
There are three key components of cloud computing:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Software as a Service (SaaS).
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS is a cloud computing model where a third-party provider hosts and manages virtualized computing resources, including servers, storage, and networking, over the internet. It allows businesses to outsource their entire infrastructure to a cloud provider, eliminating the need to manage and maintain their physical hardware. IaaS typically offer various services, including virtual machines (VMs), storage, load balancing, firewalls, and other networking tools. Customers can select the services they need and pay only for what they use on a pay-as-you-go basis. This makes IaaS a flexible and cost-effective option for businesses of all sizes.
One of the key benefits of IaaS is its scalability. Customers can easily add or remove resources as their needs change without investing in new hardware. This allows businesses to adapt quickly to changing market conditions and customer demands.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS is a cloud computing model where a third-party provider offers a platform for customers to develop, run, and manage their own applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure. Instead, PaaS providers manage the servers, storage, and networking infrastructure, allowing customers to focus on application development and deployment. PaaS providers typically offer various services, including programming languages, databases, web servers, and development tools. Customers can select the services they need and pay only for what they use on a pay-as-you-go basis. This makes PaaS a flexible and cost-effective option for businesses of all sizes.
You may also like to read: What is cloud computing?
Software as a Service (SaaS)
One of the key benefits of PaaS is its ease of use. Customers can quickly set up and deploy applications without managing the underlying infrastructure. This makes it ideal for small businesses or startups that need more resources to manage their infrastructure. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
SaaS is a cloud computing model where a third-party provider offers software applications to customers over the internet. Its providers host and maintain the applications, and customers can access them from anywhere with an internet connection, using a web browser or mobile app.
SaaS applications are licensed on a subscription basis, with customers paying a monthly or annual fee for access to the software. As a result, SaaS is a cost-effective option for businesses of all sizes, as they don’t need to invest in expensive hardware or software licenses. SaaS providers offer various applications, including email, customer relationship management (CRM), project management, accounting, and human resources. Customers can select the applications they need and pay only for what they use on a pay-as-you-go basis.
One of the key benefits of SaaS is its ease of use. Customers can quickly set up and start using applications without having to install any software or manage any hardware. This makes it ideal for small businesses or startups that don’t have the resources to manage their IT infrastructure.
Types of Cloud Computing
There are 3 types of cloud computing:
- Public Cloud
- Private Cloud
- Hybrid Cloud.
Public Cloud
Public Cloud refers to a cloud services provided by third-party providers to multiple organizations or individuals. It is the most common cloud computing type and provides users access to a large pool of shared computing resources.
In the public cloud computing model, a provider offers computing resources, such as servers, storage, and networking, to the general public over the internet. These resources are shared among multiple customers and can be accessed pay-as-you-go. This model includes services such as IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, allowing customers to choose and pay only for what they need. As a result, public cloud computing is a cost-effective option for businesses of all sizes.
Private cloud
A private cloud is a computing model where computing resources, such as servers, storage, and networking, are used exclusively by a single organization or business. Private clouds can be managed by the organization’s IT department or a third-party provider. Private clouds offer many of the same benefits as public clouds, such as scalability and flexibility, but they provide increased security and control. In addition, because the resources are not shared with other organizations, private clouds can be customized to meet specific business needs and provide higher security and compliance levels.
Private cloud computing can be deployed on-premises, using an organization’s own servers and infrastructure, or a third-party provider in a dedicated data center can host it. This allows organizations to choose the deployment model that best suits their needs.
Hybrid cloud
A hybrid cloud is a type of cloud computing model that combines the use of both public and private cloud resources. In a hybrid cloud, an organization can use a combination of its own private cloud infrastructure and public cloud services provided by a third-party provider.
The hybrid cloud model offers the best of both worlds, allowing organizations to take advantage of the scalability and cost-effectiveness of public clouds while maintaining the security and control of private clouds. For example, an organization can use a public cloud service to handle peak demand for its services or applications while keeping its sensitive data and core applications on its private cloud infrastructure. To enable a hybrid cloud environment, organizations typically use a combination of cloud management tools and APIs that allow for seamless integration between public and private cloud resources. This allows organizations to manage their entire cloud infrastructure from a single control panel, providing greater visibility and control.
You may also like to read: What is Cloud Deployment and its Types?
Public Cloud vs. Private Cloud
Public and private clouds are different cloud computing models, each with advantages and disadvantages.
The public cloud refers to a cloud computing model where third-party providers offer computing resources, such as servers, storage, and networking, over the internet to the general public. These resources are shared among multiple customers, who can access them pay-as-you-go. Public cloud computing is a cost-effective option for businesses of all sizes and offers scalability, flexibility, and high levels of reliability and availability.
On the other hand, a private cloud is a cloud computing model where computing resources are used exclusively by a single organization or business. Private clouds can be managed by the organization’s IT department or a third-party provider. Private clouds provide an added level of security and control and can be customized to meet specific business needs.
Here are some key differences between the public cloud and private cloud:
- Public cloud computing is typically less expensive than private cloud computing, as the cost is shared among multiple customers. Private cloud computing requires a higher investment in hardware and infrastructure, making it more suitable for larger organizations with dedicated IT departments.
- Private clouds provide higher security and control, as the resources are not shared with other organizations. Public clouds are generally secure but can be vulnerable to security breaches due to their multi-tenant nature.
- Private clouds can be customized to meet specific business needs, while public clouds offer a standardized set of services.
- Public clouds offer greater scalability than private clouds, as resources can be added or removed quickly and easily. Private clouds require more planning and preparation to scale up or down.
Advantages of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has several advantages, including cost savings, scalability and flexibility, accessibility and mobility, and disaster recovery and backup.
- Cost savings: Cloud computing eliminates the need for businesses to purchase and maintain physical infrastructure, which can be expensive. It enables businesses to pay for computing resources on a pay-as-you-go basis, which reduces costs.
- Scalability and flexibility: Cloud computing enables businesses to scale their computing resources up or down depending on their requirements. This provides businesses with the flexibility to adapt to changing business requirements.
- Accessibility and mobility: Cloud computing enables users to access data and applications from any device with an internet connection. This provides users with the flexibility to work from anywhere.
- Disaster recovery and backup: Cloud computing providers typically offer disaster recovery and backup services, which ensures that businesses can quickly recover from a disaster or data loss.
Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
There are several disadvantages of cloud computing, including security concerns, dependence on the internet, limited control over data and infrastructure, and performance issues.
- Security concerns: Cloud computing introduces new security risks, such as data breaches and cyber attacks. Businesses need to ensure that their data is secure and comply with regulations and standards.
- Dependence on the internet: Cloud computing requires an internet connection, which can be unreliable. This can result in downtime and loss of productivity.
- Limited control over data and infrastructure: Cloud computing providers own and manage the infrastructure, limiting businesses’ control over their data and infrastructure.
- Performance issues: Cloud computing can be slower than physical infrastructure, particularly for applications that require high-speed connectivity or low latency. This can lead to performance issues that impact user experience.
Implementing Cloud Computing
Implementing cloud computing involves several steps, including selecting the right cloud service provider, migrating data and applications to the cloud, and integrating the cloud with existing infrastructure.
Steps involved in implementing cloud computing:
- Assess the IT environment and determine which applications and data can be moved to the cloud.
- Select the right cloud service provider based on cost, scalability, and security requirements.
- Develop a migration plan that includes data migration and application migration.
- Conduct a pilot test to ensure that the cloud environment meets business requirements.
- Integrate the cloud with existing infrastructure and ensure that all systems can communicate.
Selecting the Right Cloud Service Provider:
- Cost: Cloud service providers typically offer pay-as-you-go pricing, which can be more cost-effective than purchasing and maintaining physical infrastructure.
- Scalability: Cloud service providers should be able to scale computing resources up or down depending on business requirements.
- Security: Cloud service providers should have robust security measures to protect data.
- Availability: Cloud service providers should provide high availability to ensure that applications are always accessible.
Migrating Data and Applications to the Cloud:
- Assess the data and applications to be migrated and determine any dependencies.
- Develop a migration plan that includes a timeline and data transfer methods.
- Transfer the data to the cloud environment.
- Test the applications to ensure that they function correctly in the cloud environment.
Conclusion
Cloud computing has become an essential tool for businesses of all sizes, offering numerous advantages, such as cost savings, scalability, and accessibility. However, it also comes with several disadvantages, such as security concerns and limited control over data and infrastructure. Implementing cloud computing requires careful planning and execution, and businesses should follow best practices to ensure success. For example, addressing security concerns is crucial, and businesses should ensure that their data is stored and processed in a secure and compliant environment. Successful case studies of cloud computing implementations demonstrate the benefits of careful planning, execution, and leveraging the scalability and flexibility offered by cloud computing to achieve business objectives.



I really like such kind of informative blogs about the latest technologies.
Really thorough, loved the details of the blog!
Insightful and well articulated
Insightful